ISO 26262 and ASIL: Ensuring Automotive Safety Made Simple
ISO 26262 is an international standard developed to ensure the safety of electrical and electronic systems in vehicles, playing a crucial role in maintaining automotive safety. One of the key concepts in ISO 26262 is ASIL (Automotive Safety Integrity Level). In this post, we’ll explain ASIL in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
What is ASIL? ASIL represents the safety integrity level of automotive components or systems, evaluating and categorizing the impact these components have on vehicle safety. According to ISO 26262, ASIL is classified into four levels: A, B, C, and D, where A represents the lowest risk level and D represents the highest. Note that for motorcycles, a similar classification called MSIL (Motorcycle Safety Integrity Level) is used.
How is ASIL Determined? ASIL is determined during HARA (Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment) by considering the following three factors comprehensively:
Severity: The level of injury or damage that could be caused to the driver and passengers in the event of an incident.
Exposure: How frequently such a hazardous situation could occur.
Controllability: The ability of the driver to control or mitigate the hazard.
The combination of these three factors determines the ASIL, and the higher the ASIL, the more important it is to ensure the system’s safety. For example, a system with ASIL D is a critical safety element that could lead to serious accidents if an issue arises.
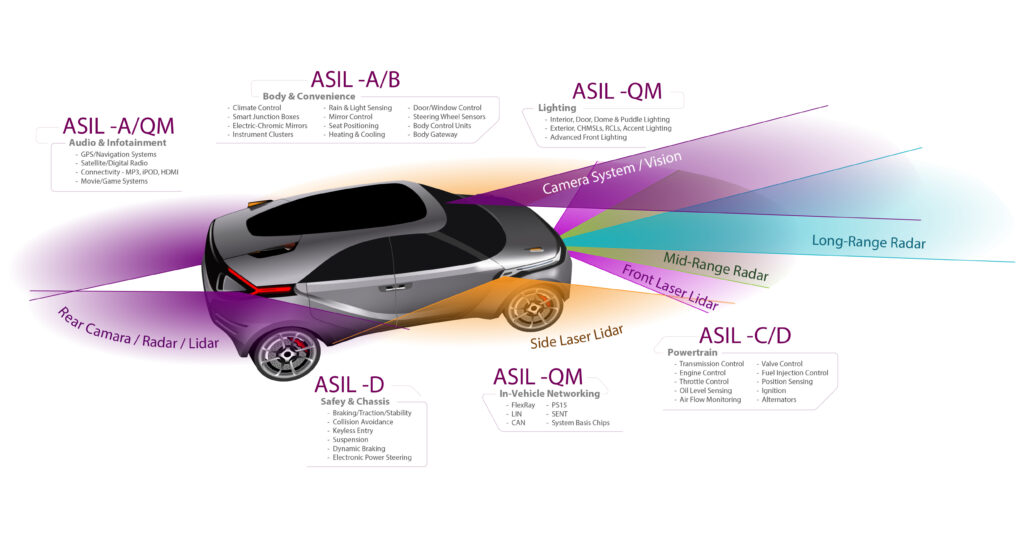
Examples of ASIL Application To better understand ASIL, here are some examples:
ASIL D: Critical safety systems such as airbags, ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), and power steering. These systems can cause severe danger if they fail.
ASIL C: Systems like cruise control, which enhance driving convenience but pose risks if they malfunction.
ASIL B: Systems such as headlights and brake lights, which could compromise driver safety if they fail.
ASIL A: Systems like rear lighting, which have a relatively lower risk level.
The Importance of ASIL ASIL is essential in defining the safety requirements during the design and development of automotive components. The ISO 26262 standard assesses the safety of each component based on its ASIL, imposing rigorous development and verification procedures accordingly. For instance, ASIL D systems must undergo thorough safety validation. The higher the ASIL level, the more safety management and scrutiny are required.
Evolution of ISO 26262 Since its first publication in 2011, ISO 26262 has been continuously evolving. In particular, the second edition, released in 2018, expanded the scope of the standard. While initially applicable only to passenger cars and commercial vehicles under 3.5 tons, ISO 26262 now covers buses and trucks over 3.5 tons, as well as motorcycles (excluding mopeds). This expansion is a response to technological advancements in the automotive industry and increased social demands for vehicle safety.
ISO 26262 and ASIL in the Age of Autonomous Driving As autonomous vehicles become more mainstream, the importance of ISO 26262 and ASIL will grow even further. Since autonomous vehicles move without driver intervention, ensuring the safety of vehicle systems is paramount. ISO 26262 and ASIL will play a critical role in ensuring that the electronic and electrical systems of autonomous vehicles operate safely.
Conclusion ISO 26262 and ASIL are essential tools for ensuring vehicle safety. By adhering to these standards, automakers can systematically prove that every component of the vehicle is designed and verified to be safe. Moving forward, complying with ISO 26262 and ASIL will be crucial in building safer cars, particularly as autonomous driving technology continues to evolve and play an increasingly significant role.